

|
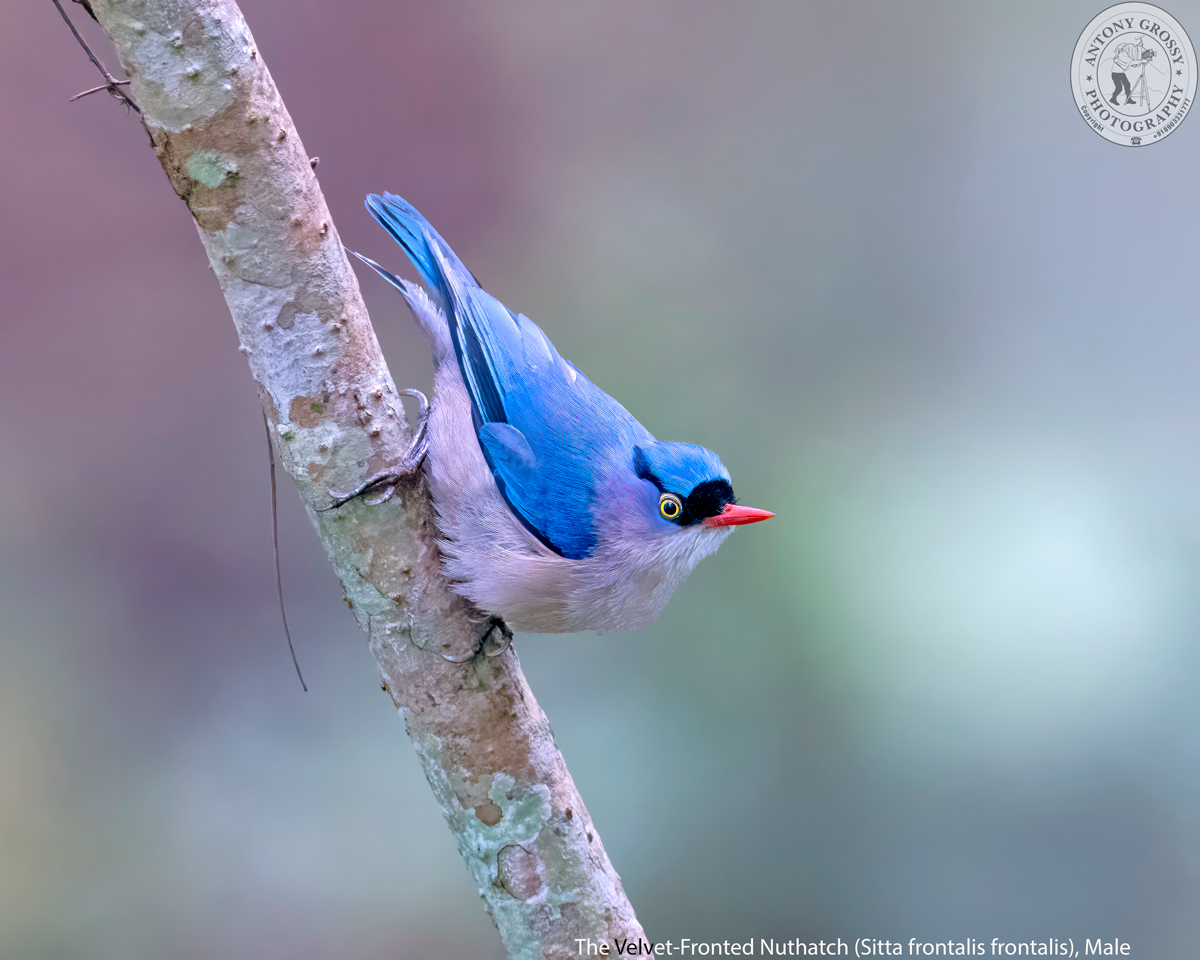 |
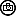
| The Aquamarine-Blue Beauty of Evergreen Forests – The Velvet-Fronted Nuthatch, Male |
| The Velvet-Fronted Nuthatch is one of the few nuthatches to break the general neutral colour scheme of the family, this stunner can be quite common in lowland and foothill evergreen forests. Aquamarine-Blue upperparts, crimson bill, and black patch on the forehead make this active little species unmistakable. Forages by creeping along trunks and branches, often upside down. Often moves in groups, frequently as a member of mixed-species flocks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. .. …. ……. . .. … …… ………………………. ………….. ……………….. .. …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. … …. ………… ………….. ………… ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. …… …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. .. ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. …… The Velvet-Fronted Nuthatch is quite a colourful Aquamarine-Blue bird and has the typical nuthatch shape, short tail and powerful bill and feet. It is a small bird reaching a length of only up to 12 to 13.5 cms in length and weighing 8.5 to 17 gms. It is a medium-small nuthatch with bright red bill (blackish in juvenile), yellow eye and eyering, black forehead and violet-blue upperparts. The male of Nominate Race in fresh plumage has lores; forecrown and narrow postocular stripe are black. The crown, upperparts and lesser and median upperwing-coverts are Aquamarine-Blue, brighter and paler Blue immediately, adjacent to Black forecrown. The greater upperwing-coverts are Blue-Grey with diffuse Violet-Blue fringes, alula and primary coverts blackish, smaller feathers of alula and distal parts of primary coverts fringed violet-blue, tertials grey-blue, longest tertial with concealed blackish stripe along shaft, secondaries and inner primaries greyish-black, grading to grey-blue sub marginally, with narrow brighter blue fringes. The central tail feathers are Grey-Blue with Violet-Blue fringes, other rectrices are black, tipped Grey-Blue and on outer web fringed Violet-Blue, outer three feather pairs with slightly paler subterminal spot on inner web. The cheek is dull Violet-Blue, fading to lavender on ear-coverts and side of neck. The chin and throat are whitish, breast is dull beige, flanks and belly to vent are darker and drabber, undertail-coverts are dull beige, diffusely tipped lavender; axillaries are whitish, anterior are feathers tipped dull Violet-Blue, underwing-coverts are black, longer under primary coverts and base of primaries are whitish. In worn plumage it is duller and greyer above, and underparts are slightly duller, pale grey-white with dull buff wash (less lilac). The iris is yellow, dull pale yellow to orange-red eyering; bill is red, tip of upper mandible is blackish; legs are dark brown, soles are orange-yellow. The Female is like male, but lacks black postocular stripe and has underparts, especially breast and belly, washed cinnamon-buff, with reduced lilac tones. The juvenile resembles adult, but bill blackish, iris is brownish, upperparts are slightly duller and greyer, chin and throat are duller, underparts are washed cinnamon-orange or orange-buff undertail-coverts are pale pinkish-buff with fine dark cinnamon-brown bars. There are Five subspecies that are recognized based on marked differences in colouration particularly on underparts and chin as well as coloration of legs and feet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. .. …. ……. . .. … …… ………………………. ………….. ……………….. .. …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. … …. ………… ………….. ………… ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. …… …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. .. ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. …… The Velvet-Fronted Nuthatch is found in Southern Asia from Nepal, India, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh East to South China and Indonesia. It frequents several types of forests such as tropical and wet forests, evergreen, deciduous, pine and mixed forests, bamboo jungles, various plantations and mature mangroves. It usually prefers more open types than closed-canopy forests. This species may be seen mainly at low elevation, but also from plains up to 1500 to 2200 mtrs according to the range. They are found in forests with good tree cover and are often found along with other species. They breed in tree cavities and holes, often created by woodpeckers or barbets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. .. …. ……. . .. … …… ………………………. ………….. ……………….. .. …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. … …. ………… ………….. ………… ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. …… …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. .. ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. …… Just as do all the other Nuthatches, their strongly clawed toes allow them to climb down tree trunks or move on the undersides of horizontal branches. They possess the agility to climb face-first down and around tree trunks and branches; unlike bird species, such as woodpeckers, which can only go upwards. It is very active and forages on tree trunks, less often on small outer branches and least on main branches and generally in upper and middle storeys of tall forest trees. It occasionally feeds in undergrowth and on fallen logs. It flushes insects from face of tree trunks by vigorous wing-flapping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. .. …. ……. . .. … …… ………………………. ………….. ……………….. .. …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. … …. ………… ………….. ………… ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. …… …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. .. ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. …… The Velvet-Fronted Nuthatch are quite noisy. Common calls a single full, hard chat, chit, chlit or chip and a much thinner and more sibilant sip, sit or tsit (many intermediates), former often in rapid couplet as chit-chit, or in short rattling series, chit-chit-chit or chit-it-it-it ; the two notes sometimes mixed, typical phrase chip, chip, sit-sit-sit-sit-sit-sit-sit, and both variants given also in flight. Song a series 1·5 to 2 seconds in duration of sit notes, individual notes usually still distinguishable, and may become a fast, hard rattle. ……….. ….. ………. …… ………….. ………… ………… …. … … …… ………….. ………… ………… ….. ………………….. … ………… ….. ………. …… ………….. …………………….. … ………… ….. ………. …… ………….. ………… ………… …. … ……… …… ……….. …… ………….. ………… ………… Description Credit Birds of the World (The Cornell Lab), Oiseaux, Birda, Animalia, Ogaclicks, Birds of India | Bird World, Bird Count India & Wiki. |
  |
|
|






















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































