

|
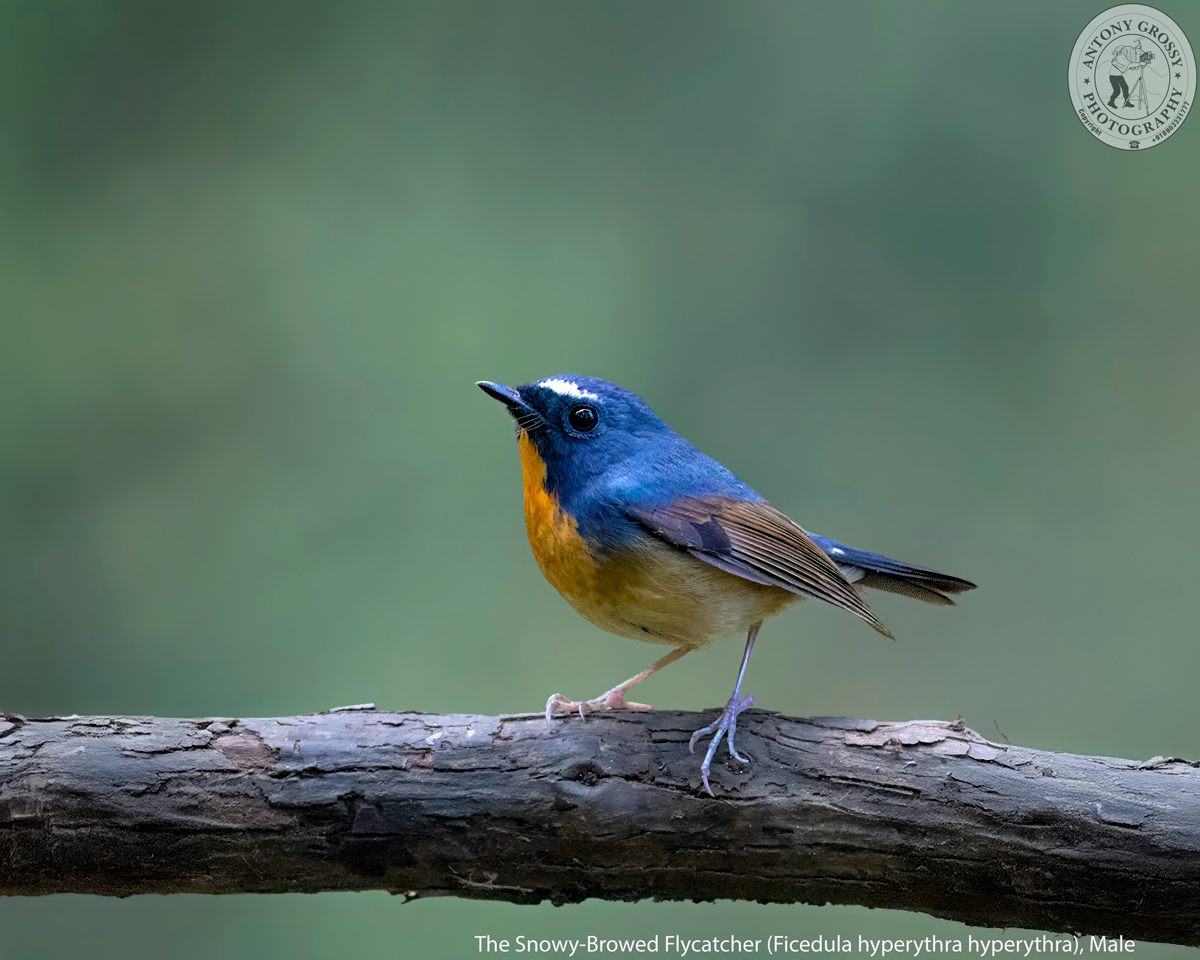 |
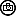
| A Frosty Vision in the High Mountains – The Snowy-Browed Flycatcher, Male |
| The Snowy-Browed Flycatcher is a truly tiny Flycatcher is a visually striking bird, easily distinguishable by the male’s distinctive frosty white “snowy brow” contrasting against its deep blue plumage. It has a large-headed, large-eyed, stub-tailed appearance. Inhabits shady forests and bamboo at upper elevations; descends into foothills in parts of range. Female is brown above with rufous-tinged wings, pale eyering, and distinctive structure. Distinguished from Slaty-Backed Flycatcher mainly by slaty-blue (not deep blue) upperparts, white supercilium and black chin; from Rufous-Throated Flycatcher by slightly smaller size, smaller bill, white in front of eye, black chin. . . . . …. ………….. ……………….. .. …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. … …. ………… ………….. ………… ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. …… …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. .. ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. … The Snowy-Browed Flycatcher is a small, short-tailed, round-headed and small-billed flycatcher, male dark blue above and female olive-brown. It measures between 11 to 13 cm in length and weighs about 6 to 12 gms. The Male of the nominate race has slate-blue head and upperparts, including upperwing and tail, blacker on lores, lower forehead, chin and side of throat, prominent short white stripe over upper lores to over eye (sometimes extending to centre of lower forehead); edges of flight-feathers warm brown or dull rufous-brown, white patch at side of tail base (often concealed or difficult to detect in field); central throat to breast deep orange to rufous-orange, flanks dusky or buffish brown, rest of underparts off-white; iris dark brown; bill black; legs dull purplish to pale grey or pinkish. Female has pale orange-buff or rusty-buff lower forehead and upper lores to around eye (forming short supercilium and eyering), lores slightly duller or dusky, cheeks and ear-coverts mottled pale buff and brownish, upperparts dark olive-brown, dull rufous edges of inner secondaries and primaries, tail tinged lightly rufous and lacking white at side of base; variable below, pale buff chin and throat and orange on breast (often forming band), or orange chin and throat more like that of male (but less extensive), rest of underparts dull buffish; legs pinkish. Juvenile is similar to Female, but has orange-buff spots and streaks on head and upperparts, orange-buff tips to greater coverts (forming wingbar) and tips of tertials, pale buff chin and throat, underparts washed orange and spotted, scalloped or mottled brown and buffish; juvenile male has slate-bluish tail. There are Thirteen subspecies currently recognized and the plumage, particularly of the females vary over the range and differing mainly in various aspects of plumage colour of upperparts, underparts and fringes of flight-feathers. . . . . …. ………….. ……………….. .. …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. … …. ………… ………….. ………… ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. …… …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. .. ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. … The Snowy-Browed Flycatcher is found in Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Philippines, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest and subtropical or tropical moist montane forest. Primary moist or mossy broadleaf forest, favouring damp areas, bamboo clumps and ravines; in non-breeding season found in similar habitat at lower levels. Breeds at 1900 to 3300 mtrs in Himalayas. Resident and altitudinal migrant. In Himalayas, post-breeding descent to foothills and adjacent plains in winter, when is present in valleys of Assam as low as 200 mtrs. . . . . …. ………….. ……………….. .. …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. … …. ………… ………….. ………… ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. …… …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. .. ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. … It eats small invertebrates and larvae, including dipteran flies, spiders, small earthworms, and some fruit like. berries. It is found in pairs in breeding season, otherwise usually solitary. It is quiet and unobtrusive, but often tame. It forages low down in clearings and forest edges, occasionally makes short aerial sallies after passing insects. This agile hunter uses its excellent acrobatic capabilities to pursue prey, snatching it mid-flight with superb precision. It is often on ground among undergrowth and runs mouse-like over ground debris and fallen branches. It flicks tail and holds wings slightly drooped at sides of body. It also sits for long periods almost motionless on perch, scanning for potential meals. . . . . …. ………….. ……………….. .. …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. … …. ………… ………….. ………… ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. …… …. …. ……….. … …. ……….. .. ………… ….. ………. …………. …….. ……………. … Its Song is a quiet, high-pitched and wheezing series of descending tsit-tsip-tsee-tswii or chee-chee-chee-chaw, often with final note prolonged, may also be followed after short pause by see-saw; also an even-pitched and twittering sitta-sitta, siya siya. Calls include thin upslurred chee or seep and softer or thin sip, frequently repeated. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . …………………….. ………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………. .. ……… …… … …. ……….. Description Credit Birds of the World (The Cornell Lab), Oiseaux, Birda, Animalia, Nepal Desk, Ogaclicks, Birds of India | Bird World, Bird Count India & Wiki. |
  |
|
|






































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































